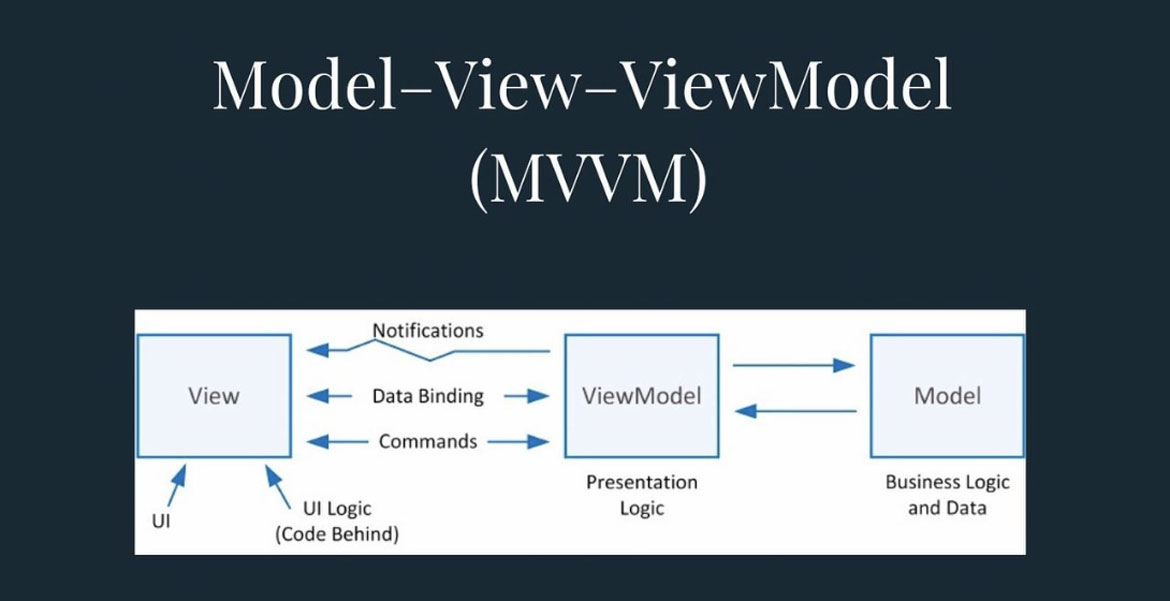
Flutter is an open source framework by Google for building beautiful, natively compiled, multi-platform applications from a single codebase.
There are a few differentiating advantages of Flutter app development. Let’s look at some of the major ones.
We have asked our flutter enthusiasts to provide their feedback on why they love flutter so much and why they’d recommend this framework above any other for your next software development project, especially when it comes to mobile application development. Here is what they said:
Cross-platform development
Flutter is cross-platform development, in which developers can build attractive apps in iOS and Android platforms contemporaneously.
As a result, Flutter programming is a great choice from cost-savings perspective, as you don’t have to hire two development teams to build a separate application for each of the mobile platforms.
Faster code writing
Flutter code compiles to ARM or Intel machine code as well as JavaScript, for fast performance on any device.
Hot reload
Typically, iOS and Android developers need to write code, then wait for it to compile, and be loaded on the device before seeing changes. But, with Flutter’s hot reload, they can check the effects immediately or without delay.
Reach users on every screen
Deploy to multiple devices from a single codebase: mobile, web, desktop, and embedded devices.
Native performance
Flutter compiles down to native machine code for fast apps and beautiful animations.

Strong Community
Flutter is supported and used by Google, trusted by well-known brands around the world, and maintained by a community of global developers.
Some of them: Abbey Road, Alibaba, BMW, Byte Dance, Capital One, Dream11, Ebay, Emaar, Grab, Google, Groupon, Toyota, MGM, Nubank, NY Times, Philips Hue, Sonos, Square, Tencent.
Flutter continues to grow, both in usage and in the size of the ecosystem. Every day, more than 1,000 new mobile apps using Flutter are published to the Apple and Google Play stores, along with more usage on web and desktop. And the Flutter package ecosystem now comprises over 25,000 packages, providing further evidence of maturity and breadth.
Always open source
Trusted by a global community of contributors and supported by Google, Flutter is open, transparent, and reliable.
Interested to work with Flutter or apply it to your business idea?
We’ve got you covered! Tell us about the project you have in mind and we will help you turn your idea into reality!