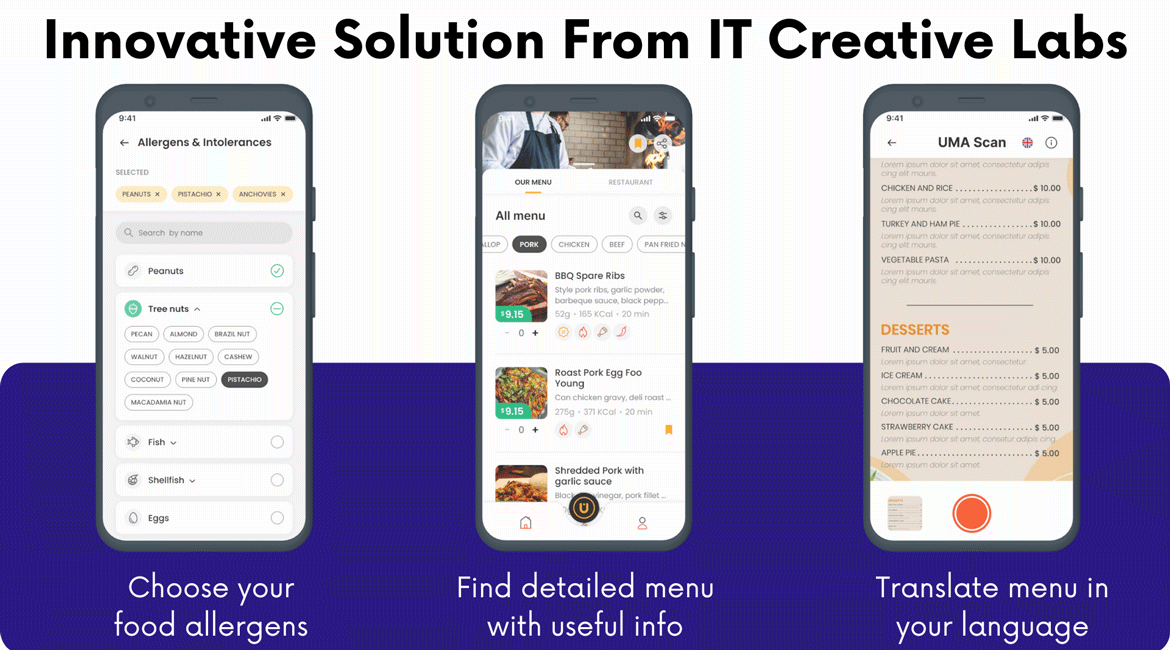
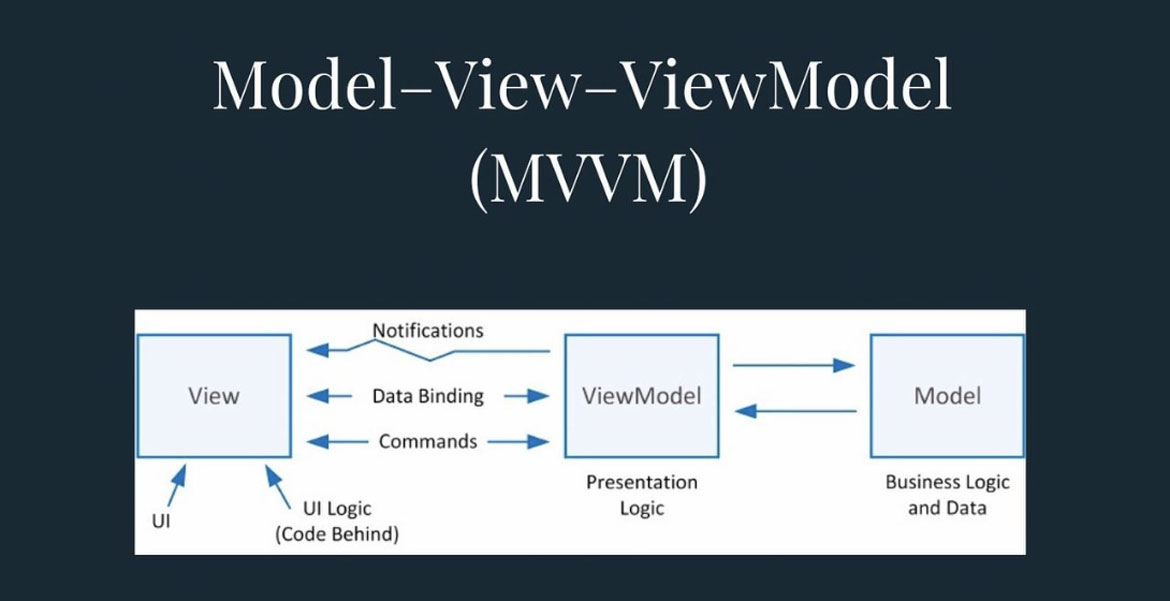
React Native is an open-source framework developed by Facebook, which has become the go-to choice for companies seeking a cost-effective and time-efficient solution for building dynamic mobile applications.
The demand for React Native developers has created a competitive environment, posing a challenge for companies aiming to build a talented and skilled development team.
In this guide, we explore the complexities of hiring React Native developers in 2024 and address the challenges faced by companies in this pursuit.
Table of Contents
- Why Hire React Native Developers?
- Key Skills of React Native Developer in 2024
- When to Hire a React Native Developer
- Challenges in Finding React Native Developers
- Tips for Hiring React Native Developers in 2024
- Conclusion
Why Hire React Native Developers?
Hiring React Native developers is a strategic move that goes beyond industry trends – it’s a practical choice for companies aiming to optimize their mobile app development.
Hiring React Native developers is a strategic move that goes beyond industry trends – it’s a practical choice for companies aiming to optimize their mobile app development.
With React Native, mobile apps can seamlessly run on both iOS and Android platforms, offering an efficient and cost-wise solution without compromising the quality of the end product.
Here are some of the reasons why your company should consider investing in React Native developers:
1. Cross-Platform Efficiency
React Native allows developers to write a single codebase that works smoothly on multiple devices (both iOS and Android). This eliminates the need for separate development teams or projects for each platform, significantly reducing time and costs.
2. Agile Development Cycles
React Native, known for its versatility and cross-platform capabilities, aligns well with the agile methodology’s emphasis on flexibility and rapid development. Its ability to streamline the development process for both iOS and Android platforms allows teams to iterate quickly, adapt to changing requirements, and deliver features in shorter cycles.
3. Community Support
With an extensive open-source community, React Native provides a rich repository of resources, third-party libraries, and shared knowledge.
React Native’s official GitHub repository is a central hub for developers to access the source code, report issues, and collaborate on improvements. Developers actively participate in discussions surrounding proposed changes, feature requests, and bug fixes.
4. Faster Development Time
React Native’s advantage of faster development time is a result of its hot-reloading feature, allowing developers to see real-time updates without restarting the application.
Additionally, the framework’s ability to share a single codebase across multiple platforms streamlines development efforts, eliminating the need to create and maintain separate code for iOS and Android. As a result, React Native significantly expedites the overall development cycle, enabling teams to bring feature-rich and high-performance applications to market swiftly.
5. High-Performance and Scalable Development
React Native delivers exceptional high-performance mobile applications through its innovative hybrid architecture, combining native modules with JavaScript. This approach ensures that React Native apps achieve near-native efficiency and get seamless user experiences.
Additionally, the framework’s scalability is evident as it accommodates the growth of user bases and evolving feature sets, making it ideal for applications aiming for long-term success.
Key Skills of React Native Developer in 2024
In 2024, React Native developers must possess a versatile skill set to meet the evolving requirements of mobile app development. Here, we highlight essential technical and soft skills you need to look for when you hire a React Native developer:
Technical Skills:
Proficiency in React Native Framework
Mastery of the React Native framework is paramount, encompassing the ability to efficiently develop and optimize cross-platform mobile applications. A deep understanding of component lifecycles, state management, and navigation within React Native is essential.
JavaScript Proficiency
A strong command of JavaScript is foundational for React Native development. Developers should demonstrate expertise in ES6 and beyond, asynchronous programming, and knowledge of JavaScript frameworks to ensure efficient and effective code implementation.
Mobile Platform Knowledge
Adeptness in understanding the intricacies of both iOS and Android platforms is crucial. React Native developers should possess knowledge of platform-specific design principles, APIs, and performance considerations to deliver seamless cross-platform experiences.
State Management Expertise
Proficiency in state management solutions, such as Redux or MobX, is vital for handling complex data flows within React Native applications. Developers should demonstrate the ability to architect scalable and maintainable state management systems.
Integration of Native Modules
The ability to seamlessly integrate and leverage native modules in React Native applications enhances functionality. Developers should be adept at incorporating native modules to access platform-specific functionalities when needed.
Soft Skills:
Problem Solving
React Native developers should excel in creative and efficient problem-solving, navigating challenges to deliver innovative solutions within project timelines.
Collaboration
Effective collaboration is key. React Native developers should thrive in team environments, communicate clearly, and contribute positively to project discussions, fostering a cohesive and productive development process.
Adaptability and Learning Agility
Given the rapidly evolving tech landscape, React Native developers should exhibit a keen willingness to learn and adapt. Staying updated on industry trends and swiftly incorporating new technologies is essential.
Attention to User Experience
Besides technical issues, React Native developers must prioritize user experience. A keen eye for design details and an understanding of user-centric development principles contribute to creating engaging and user-friendly applications.
Communication
Clear and concise communication is paramount in conveying ideas, updates, and potential challenges. React Native developers should articulate technical concepts effectively to both technical and non-technical stakeholders, ensuring a smooth development workflow.
When to Hire a React Native Developer
Here are key reasons why you need to bring a React Native developer on board:
You Need to Optimize Development Costs
When cost efficiency is a priority without compromising the quality of mobile app development, React Native developers shine. With hot-reloading features and code reusability, React Native developers enable faster iterations and decreased expenses associated with maintaining separate codebases for iOS and Android.
If reducing costs is key priority, React Native is an ideal choice for you.
You Need to Switch Seamlessly Between Platforms
React Native allows developers to build cross-platform mobile applications using a single codebase. If your company aims to reach both iOS and Android users efficiently without doubling development efforts, hiring React Native developers is imperative for a seamless transition between platforms.
You Need a Versatile Solution for Diverse Projects
React Native provides a versatile framework suitable for various project types. Whether you’re working on a startup MVP, expanding an existing app, or implementing new features, hiring React Native developers ensures adaptability and efficiency across diverse project requirements.
Challenges in Finding React Native Developers
Recruiting skilled React Native developers presents a unique set of challenges for several reasons. Here are some of them:
High Demand, Limited Supply
The soaring demand for React Native developers far exceeds the available talent pool. Companies often find themselves vying for the attention of skilled developers, resulting in shortage that can elongate the hiring process.
Evolving Skill Requirements
The rapid evolution of React Native and its ecosystem introduces ever-changing skill requirements. Identifying developers who possess technical and soft skills becomes a challenge, requiring companies to stay abreast of the latest industry trends.
Competition with Industry Giants
Large tech corporations often have the resources to attract and retain top React Native talent, leaving smaller companies or startups in fierce competition. Convincing skilled developers to join smaller teams requires strategic positioning and emphasis on the unique opportunities offered by the hiring company.
Ensuring Cultural Fit
In addition to evaluating technical proficiency, it is crucial to consider the alignment of a React Native developer’s values, work approach, and cultural compatibility with the company. Ensuring synergy between the developer and the team is essential for long-term success but can be challenging to assess during the hiring process.
Remote Work Challenges
With the rise of remote work, companies are faced with the challenge of ensuring effective collaboration of React Native developers in a distributed team. Communication barriers and team unity are challenging due to the distance, and companies need to find ways to tackle these issues for successful collaboration.
Tips for Hiring React Native Developers in 2024
Having considered the essential skills of React Native developers, the challenges companies face in the hiring process, and the compelling reasons to bring dedicated React Native developers on board, we now aim to finalize our guide with actionable tips.
Hiring React Native developers requires a strategic approach to identify candidates with the right skills and qualities, so here are some tips to guide you through the hiring process:
Define Clear Job Requirements
Clearly outline the specific skills, experience, and qualifications you are looking for in a React Native developer. This helps in attracting candidates who match your project’s needs.
Evaluate React Native Proficiency
Assess a candidate’s proficiency in React Native by reviewing their previous projects, GitHub contributions, or asking them to complete a coding challenge related to React Native. This practical evaluation ensures they have hands-on experience.
Discuss Experience with Third-Party Libraries
React Native allows integration with numerous third-party libraries. Inquire about the candidate’s experience in using and integrating these libraries, showcasing their ability to leverage existing solutions for efficient development.
Ask About Testing Practices
Testing is integral to app development. Inquire about a candidate’s experience with testing frameworks, unit testing, and their approach to ensuring the reliability and robustness of React Native applications.
Emphasize Soft Skills
Soft skills like teamwork, adaptability, and problem-solving are equally important. Ensure that the candidate possesses the interpersonal skills required for effective collaboration within your development team.
Consider Portfolio and References
Review a candidate’s portfolio to understand the scope and quality of their previous React Native projects. Additionally, seek references from their previous employers or clients to gain insights into their work ethic and collaboration skills.
By incorporating these tips into your hiring process, you can identify React Native developers who align with your company’s culture and project requirements.
Conclusion
Navigating through the skills essential for React Native developers, effective screening techniques, challenges in finding the right talent, and strategic indications for when to hire, we’ve covered the main questions.
Our tips for hiring React Native developers in 2024 serve as a practical guide to making informed decisions in selecting developers who align with the unique needs of your projects and company in general.
Ready to Bring Your Vision to Life?
If you are ready to hire a skilled React Native developer for your project, IT Creative Labs is here to help.
Our team comprises dedicated React Native developers with a wealth of experience, a diverse portfolio of successful projects, and a combination of both soft and technical skills.
We are committed to building your project with precision and excellence. Contact us today to turn your ideas into reality with our expert React Native developers.