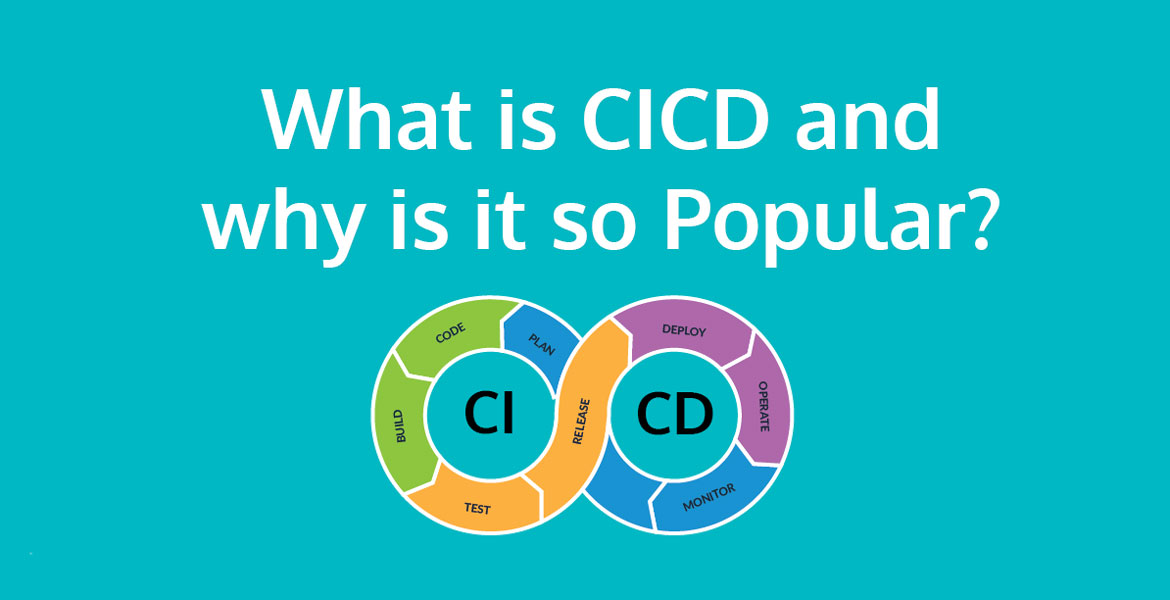
What is CI/CD?
CI/CD is a set of practices that automate the building, testing, and deployment stages of software development. Automation reduces delivery timelines and increases reliability across the development life cycle.
Most modern applications require developing code using a variety of platforms and tools, so teams need a consistent mechanism to integrate and validate changes. Continuous integration establishes an automated way to build, package, and test their applications. Having a consistent integration process encourages developers to commit code changes more frequently, focus on meeting business requirements, code quality, and security, which leads to better collaboration and code quality.
Continuous integration and continuous delivery are two distinct processes in CI/CD and have different purposes:
- CI runs automated build-and-test steps to ensure that code changes reliably merge into the central repository.
- CD provides a quick and seamless method of delivering the code to end-users.
So the main goal of CI/CD is to help developers ship software with speed and efficiency. The team continuously delivers code into production, running an ongoing flow of new features and bug fixes.
The most popular CI/CD tools
A CI/CD tool helps DevOps teams create a pipeline and automate integration, deployment, and testing stages. Some tools specifically handle the integration (CI) side, some manage development and deployment (CD), while others specialize in continuous testing or related functions.
Here is a list of the most popular CI/CD tools you can choose from:
- Jenkins: An automation server that can handle anything from simple CI to a complex CI/CD pipeline.
- TeamCity: A CI server that helps build and deploy projects with reusable settings and configurations.
- Spinnaker: An open-source CD platform ideal for multi-cloud environments.
- GoCD: A CI/CD server that emphasizes modeling and visualization.
- CircleCI: A flexible, cloud-based CI/CD tool perfect for smaller projects.
- Travis CI: A Ruby-based tool with a robust build matrix.
- Bamboo: A CI server with support for several top stacks (Docker, AWS, Amazon S3, Git, CodeDeploy, Mercurial) and up to a hundred remote build agents.
CI/CD enables more frequent code deployment.
So, let’s sum up
CI packages, tests builds, and notifies developers if something goes wrong. The CD automatically deploys applications and performs additional tests.
CI/CD pipelines are designed for organizations that need to make frequent changes to applications with a reliable delivery process. In addition to build standardization, test development, and deployment automation, we get a holistic production process for deploying code changes. The introduction of CI/CD allows developers to focus on improving applications and not spend effort on deploying it.
CI/CD is one of the DevOps practices, as it aims to combat the tension between developers who want to make frequent changes and operations that require stability. With automation, developers can make changes more frequently, and operations teams, in turn, gain greater stability because environment configuration is standardized and continuous testing is carried out during delivery. Also, the setting of environment variables is separated from the application and there are automated rollback procedures.
However, CI/CD is just one of the processes that can contribute to improvements. There are other conditions for increasing the frequency of delivery.
To get started with CI/CD, the development and operations teams need to decide on technologies, practices, and priorities. Teams need to build consensus on the right approaches for their business and technology so that once CI/CD is implemented, the team consistently adheres to the chosen practices.